神经风格迁移是指将参考图像的风格应用于目标图像,同时保留目标图形的内容,如下图所示:

实现风格迁移核心思想就是定义损失函数,然后最小化损失。这里的损失包括风格损失和内容损失。
用公式来表示就是:
|
1 2 |
loss = distance(style(reference_image) - style(generated_image)) + distance(content(original_image) - content(generated_image)) |
具体内容如下图
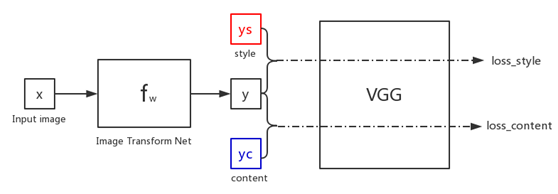
如图,假设初始化图像x(Input image)是一张随机图片,我们经过fw(image Transform Net)网络进行生成,生成图片y。
此时y需要和风格图片ys进行特征的计算得到一个loss_style,与内容图片yc进行特征的计算得到一个loss_content,假设loss=loss_style+loss_content,便可以对fw的网络参数进行训练。
23.1 内容损失
内容损失一般选择靠近的某层激活的差平方或L2范数。
写成代码就是
|
1 |
content_loss = F.mse_loss(features[2], content_features[2]) * content_weight |
23.2 风格损失
格拉姆矩阵(Gram Matrix),即某一层特征图的内积。这个内积可以理解为表示该层特征之间相互关系的映射。损失函数的定义主要考虑以下因素:
①在目标内容图像和生成图像之间保持相似的较高层激活,从而能保留内容。卷积神经网络应该能够看到目标图像和生成图像包含相同的内容。
②在较低层和较高层的激活中保持类似的相互关系,从而能保留风格。特征相互关系捕zu到的是纹理,生成图像和风格参考图像在不同的空间尺度上应该具有相同纹理。
Gram Matrices的计算过程
假设输入图像经过卷积后,得到的feature map为[ch, h, w]。我们经过flatten和矩阵转置操作,可以变形为[ ch, h*w]和[h*w, ch]的矩阵。再对两矩阵做内积得到[ch, ch]大小的矩阵,这就是我们所说的Gram Matrices,如下图所示:
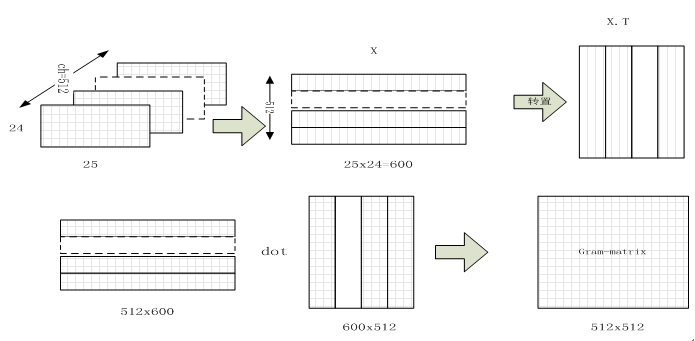
比如我们假设输入图像经过卷积后得到的[b, ch, h*w]的feature map,其中我们用fm表示第m个通道的特征层,fn为第n通道特征层。则Gram Matrices中元素fm∗fn代表的就是m通道和n通道特征flatten后按位相乘(内积)
具体实现代码
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
def gram_matrix(y): (b, ch, h, w) = y.size() features = y.view(b, ch, w * h) features_t = features.transpose(1, 2) gram = features.bmm(features_t) / (ch * h * w) return gram style_grams = [gram_matrix(x) for x in style_features] style_loss = 0 grams = [gram_matrix(x) for x in features] for a, b in zip(grams, style_grams): style_loss += F.mse_loss(a, b) * style_weight |
关于Gram矩阵还有以下三点值得注意:
1 Gram矩阵的计算采用了累加的形式,抛弃了空间信息。一张图片的像素随机打乱之后计算得到的Gram Matrix和原图的Gram Matrix一样。所以认为Gram Matrix所以认为Gram Matrix抛弃了元素之间的空间信息。
2 Gram Matrix的结果与feature maps F 的尺寸无关,只与通道个数有关,无论H,W的大小如何,最后Gram Matrix的形状都是CxC
3 对于一个C x H x W的feature maps,可以通过调整形状和矩阵乘法运算快速计算它的Gram Matrix。即先将F调整到 C x (H x W)的二维矩阵,然后再计算F 和F的转置。结果就为Gram Matrix
Gram Matrix的特点:
通过相乘运算,它将特征之间的区别进行扩大或者缩小,由此可一定程度反应向量本身及向量之间的一些特征或关系,它注重风格纹理,忽略空间信息

23.3 用keras实现神经风格迁移
https://ypw.io/style-transfer/(神经风格迁移 pytorch 0.4)
1)导入目标、风格图像
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array # This is the path to the image you want to transform. #target_image_path = '/home/wumg/data/data/portrait.png' target_image_path = '/home/wumg/data/data/shanghai_buildings.jpg' # This is the path to the style image. #style_reference_image_path = '/home/wumg/data/data/popova.png' style_reference_image_path = '/home/wumg/data/data/starry-sky.jpg' # Dimensions of the generated picture. width, height = load_img(target_image_path).size img_height = 400 img_width = int(width * img_height / height) |
2)定义图像处理辅助函数
对进出VGG19神经网络的图像进行加载、预处理和后处理等处理。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import numpy as np from keras.applications import vgg19 def preprocess_image(image_path): img = load_img(image_path, target_size=(img_height, img_width)) img = img_to_array(img) img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0) img = vgg19.preprocess_input(img) return img def deprocess_image(x): # Remove zero-center by mean pixel x[:, :, 0] += 103.939 x[:, :, 1] += 116.779 x[:, :, 2] += 123.68 # 'BGR'->'RGB' x = x[:, :, ::-1] x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8') return x |
【说明】
keras中preprocess_input()函数的作用是对样本执行 逐样本均值消减 的归一化,即在每个维度上减去样本的均值,对于维度顺序是channels_last的数据,keras中每个维度上的操作如下:
|
1 2 3 |
x[..., 0] -= 103.939 x[..., 1] -= 116.779 x[..., 2] -= 123.68 |
3)加载VGG19网络,并将其应用于三张图像
三张图像是目标图像、风格图像、生成图像,把这三张图像作为一个批量。其中生成图像将改变,以占位符的形式存储。而目标图像、风格图像在整个过程中是不变的,故以constant方式存储。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
from keras import backend as K target_image = K.constant(preprocess_image(target_image_path)) style_reference_image = K.constant(preprocess_image(style_reference_image_path)) # This placeholder will contain our generated image combination_image = K.placeholder((1, img_height, img_width, 3)) # We combine the 3 images into a single batch input_tensor = K.concatenate([target_image, style_reference_image, combination_image], axis=0) # We build the VGG19 network with our batch of 3 images as input. # The model will be loaded with pre-trained ImageNet weights. model = vgg19.VGG19(input_tensor=input_tensor, weights='imagenet', include_top=False) print('Model loaded.') |
Downloading data from https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/releases/download/v0.1/vgg19_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5
80142336/80134624 [==============================] - 155s 2us/step
Model loaded.
4)查看VGG19的网络结构图
|
1 |
print(model.summary()) |
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, None, None, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block1_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 64) 1792
_________________________________________________________________
block1_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 64) 36928
_________________________________________________________________
block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, None, None, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block2_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 128) 73856
_________________________________________________________________
block2_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 128) 147584
_________________________________________________________________
block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, None, None, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 256) 295168
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv4 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, None, None, 256) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv4 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, None, None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv4 (Conv2D) (None, None, None, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, None, None, 512) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 20,024,384
Trainable params: 20,024,384
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
None
VGG19网络的结构图
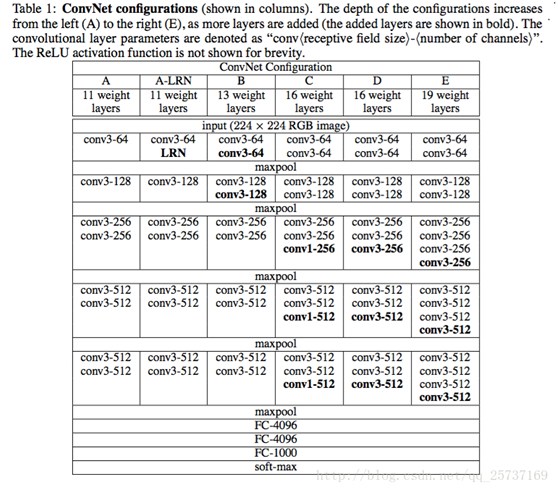
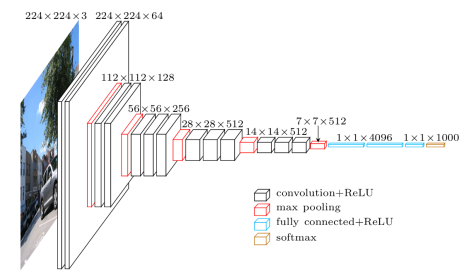
5)定义内容损失
内容损失最小化,以保证目标图像和生成图像在VGG19卷积神经网络的顶层(即block5-conv2)具有相似结果。
|
1 2 |
def content_loss(base, combination): return K.sum(K.square(combination - base)) |
6)定义风格损失函数
使用一个辅助函数来计算输入矩阵的格拉姆矩阵,即原始特征矩阵中相互关系的映射。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
def gram_matrix(x): features = K.batch_flatten(K.permute_dimensions(x, (2, 0, 1))) gram = K.dot(features, K.transpose(features)) return gram def style_loss(style, combination): S = gram_matrix(style) C = gram_matrix(combination) channels = 3 size = img_height * img_width return K.sum(K.square(S - C)) / (4. * (channels ** 2) * (size ** 2)) |
假设输入图像经过卷积后,得到的feature map为[ch, h, w]。我们经过flatten和矩阵转置操作,可以变形为[ ch, h*w]和[h*w, ch]的矩阵。再对两矩阵做内积得到[ch, ch]大小的矩阵,这就是我们所说的Gram Matrices,如下图所示:

7)定义总变差损失函数
除了以上两个损失函数,还需要一个总变差损失,它对生成的图像的像素进行正则化等操作,它促使生成图像具有空间的连续性,以避免结果过度像素化。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
def total_variation_loss(x): a = K.square( x[:, :img_height - 1, :img_width - 1, :] - x[:, 1:, :img_width - 1, :]) b = K.square( x[:, :img_height - 1, :img_width - 1, :] - x[:, :img_height - 1, 1:, :]) return K.sum(K.pow(a + b, 1.25)) |
8)定义总损失函数
总损失是内容损失、风格损失、总变差损失的加权损失。网络顶层包含更加全局、更加抽象的信息,所以内容损失只使用一个顶层,即block5_conv2层;每层对都有不同风格,所以对风格损失需要使用一系列的层(block1_conv1、block2_conv1、block3_conv1、block4_conv1、block5_conv1)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
# Dict mapping layer names to activation tensors outputs_dict = dict([(layer.name, layer.output) for layer in model.layers]) # Name of layer used for content loss content_layer = 'block5_conv2' # Name of layers used for style loss style_layers = ['block1_conv1', 'block2_conv1', 'block3_conv1', 'block4_conv1', 'block5_conv1'] # Weights in the weighted average of the loss components total_variation_weight = 1e-4 style_weight = 1. content_weight = 0.025 # Define the loss by adding all components to a `loss` variable loss = K.variable(0.) layer_features = outputs_dict[content_layer] target_image_features = layer_features[0, :, :, :] combination_features = layer_features[2, :, :, :] loss += content_weight * content_loss(target_image_features, combination_features) for layer_name in style_layers: layer_features = outputs_dict[layer_name] style_reference_features = layer_features[1, :, :, :] combination_features = layer_features[2, :, :, :] sl = style_loss(style_reference_features, combination_features) #loss += (style_weight / len(style_layers)) * sl loss =loss + (style_weight / len(style_layers)) * sl #loss+=total_variation_weight * total_variation_loss(combination_image) loss = loss + total_variation_weight * total_variation_loss(combination_image) |
9)L_BFGS算法简介
这里使用scipy中L_BFGS算法进行最优化。为便于大家理解该优化器,这里我们先简单介绍一下L_BFGS算法对应的函数格式及示例。
fmin_l_bfgs_b函数格式:
|
1 |
scipy.optimize.fmin_l_bfgs_b(func, x0, fprime=None, args=(), approx_grad=0, bounds=None, m=10, factr=10000000.0, pgtol=1e-05, epsilon=1e-08, iprint=-1, maxfun=15000, maxiter=15000, disp=None, callback=None, maxls=20)[source]¶ |
使用示例:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
x_true = np.arange(0,10,0.1) m_true = 2.5 b_true = 1.0 y_true = m_true*x_true + b_true def func(params, *args): x = args[0] y = args[1] m, b = params y_model = m*x+b error = y-y_model return sum(error**2) initial_values = np.array([1.0, 0.0]) mybounds = [(None,2), (None,None)] fmin_l_bfgs_b(func, x0=initial_values, args=(x_true,y_true), approx_grad=True) fmin_l_bfgs_b(func, x0=initial_values, args=(x_true, y_true), bounds=mybounds, approx_grad=True) |
10)定义生成图像的优化器
通过优化器获取梯度、损失等
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
# Get the gradients of the generated image wrt the loss grads = K.gradients(loss, combination_image)[0] # Function to fetch the values of the current loss and the current gradients fetch_loss_and_grads = K.function([combination_image], [loss, grads]) class Evaluator(object): def __init__(self): self.loss_value = None self.grads_values = None def loss(self, x): assert self.loss_value is None x = x.reshape((1, img_height, img_width, 3)) outs = fetch_loss_and_grads([x]) loss_value = outs[0] grad_values = outs[1].flatten().astype('float64') self.loss_value = loss_value self.grad_values = grad_values return self.loss_value def grads(self, x): assert self.loss_value is not None grad_values = np.copy(self.grad_values) self.loss_value = None self.grad_values = None return grad_values evaluator = Evaluator() |
11)训练模型
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
from scipy.optimize import fmin_l_bfgs_b from scipy.misc import imsave import imageio import time result_prefix = 'style_transfer_result' iterations = 20 # Run scipy-based optimization (L-BFGS) over the pixels of the generated image # so as to minimize the neural style loss. # This is our initial state: the target image. # Note that `scipy.optimize.fmin_l_bfgs_b` can only process flat vectors. x = preprocess_image(target_image_path) x = x.flatten() for i in range(iterations): print('Start of iteration', i) start_time = time.time() x, min_val, info = fmin_l_bfgs_b(evaluator.loss, x, fprime=evaluator.grads, maxfun=20) print('Current loss value:', min_val) # Save current generated image img = x.copy().reshape((img_height, img_width, 3)) img = deprocess_image(img) fname = result_prefix + '_at_iteration_%d.png' % i #imsave(fname, img) imageio.imwrite(fname, img) end_time = time.time() print('Image saved as', fname) print('Iteration %d completed in %ds' % (i, end_time - start_time)) |
12)可视化目标图、参考风格图、生成图等。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # Content image plt.imshow(load_img(target_image_path, target_size=(img_height, img_width))) plt.figure() # Style image plt.imshow(load_img(style_reference_image_path, target_size=(img_height, img_width))) plt.figure() # Generate image plt.imshow(img) plt.show() |



Pingback引用通告: Python与人工智能 – 飞谷云人工智能